The ISA Model
The ISA standard is commonly used for collecting, currating, managing and reusing datasets in the field of life, environmental and biomedical sciences such as toxicology and plant sciences.
The ISA standard focusses on describing an entire project's metadata. It does not prescribe a format for a project's measurement data, e.g. whether a data file should be in a cetain time series structure of file format.
The ISA standard is built upon:
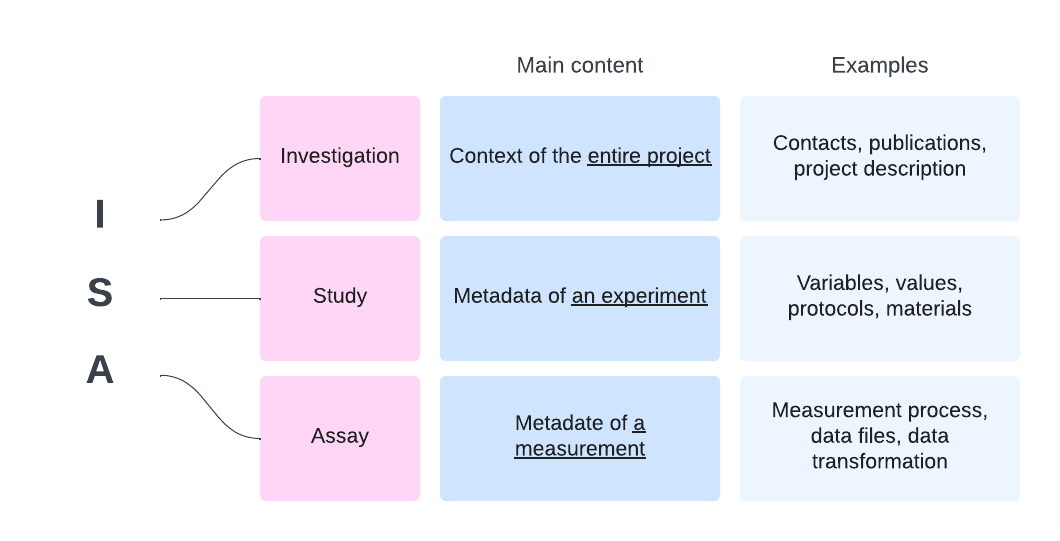
Investigation (I)
Study (S), being part of Investigation
Assay (A), being part of Study
The Investigation, Study and Assay, and related concepts, are introduced in the following sections.
Investigation
The investigation describes the general context of a project and ‘contains all the information needed to understand the overall goals and means used in an experiment’. First of all, it describes metadata of an experiment. Second, it introduces the studies and the assays that are part of the investigation.
Study
The study is the unit of research and contains ‘information on the subject under study, its characteristics and any treatments applied’.
One investigation can contain multiple studies. The study describes characteristics of the subject under study, and manipulations performed on a set-up to affect the subject, in a way that an effect can be measured.
Assay
The Assay describes the measurements and 'represents a test performed either on material taken from a subject or on a whole initial subject, producing qualitative or quantitative measurements'.
One study can contain multiple assays. Where the study describes the experiment itself, the assay describes how the data from an experiment is extracted.
Other relevant concepts
Protocol
A Process is a sequence of steps that are carried out during an experiment. Examples are data collection, data transformation and experiment preparation.
Protocol Parameter
A Protocol Parameter is a variable that is used in a protocol.
Process
A Process is an entity that applies some protocol to an input material, and produces output. For example, a data transformation process applies a data transformation protocol to a raw data file and generates a data file.
Study Factor
A Study Factor is an independent variable manipulated by the experimentalist with the intention to affect a system in a way that can be measured by an assay. For example, plant growth.
Factor Value
A FactorValue is a value of a StudyFactor.
Data File
A Data File represents a pointer to a file that contains measurements from an assay.
Source
A Source is the subject from which a Sample is taken.
Sample
A Sample is the subject to which a process is applied, after which measurements are obtained. A Sample is typically obtained from a Source.
Characteristic
A Characteristic acts as a qualifying property for a material, sample or subject.
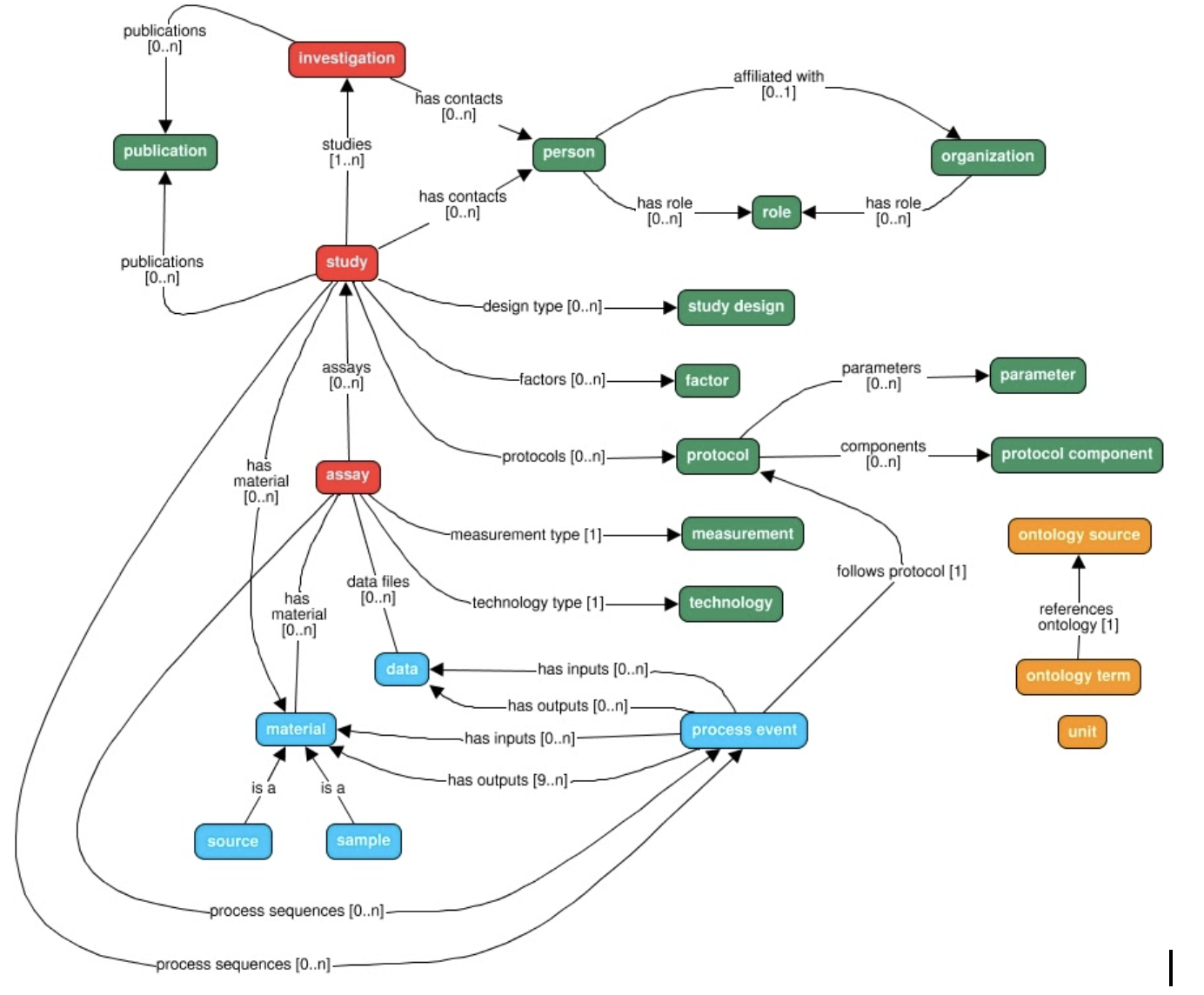
Model overview